About
In 1775, the Marquis de Sade wrote of it, “I have never seen anything more striking.” Granted, the crypt was to his tastes.
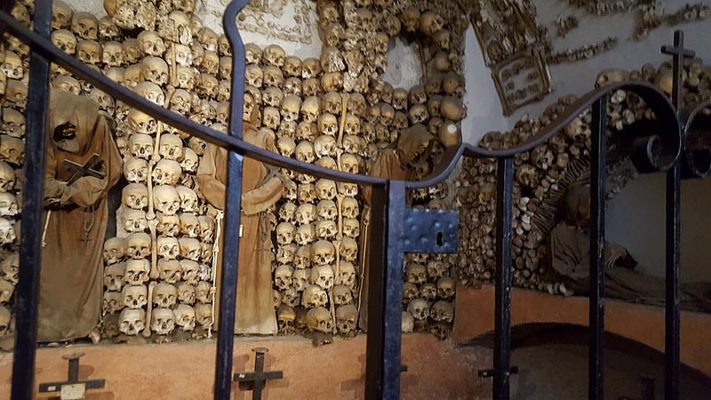
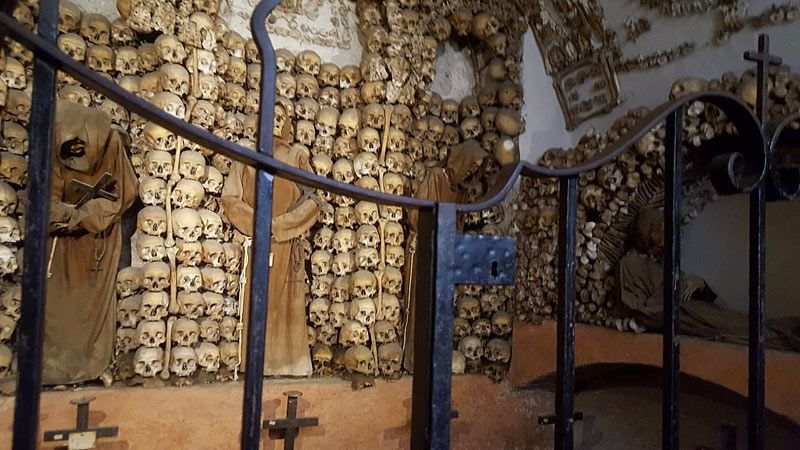
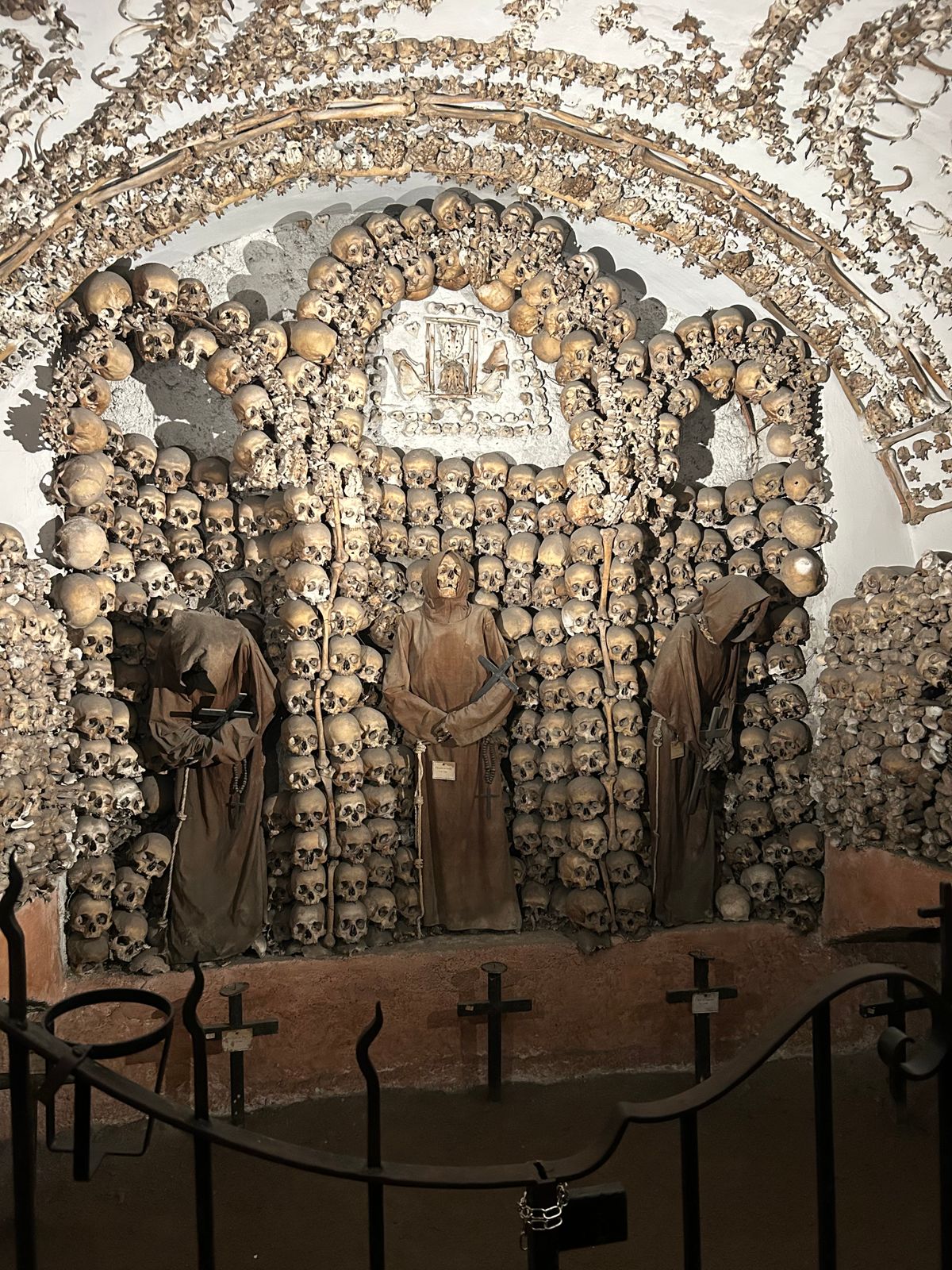
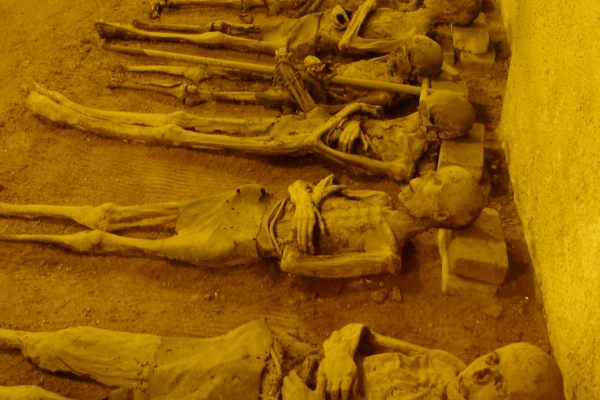
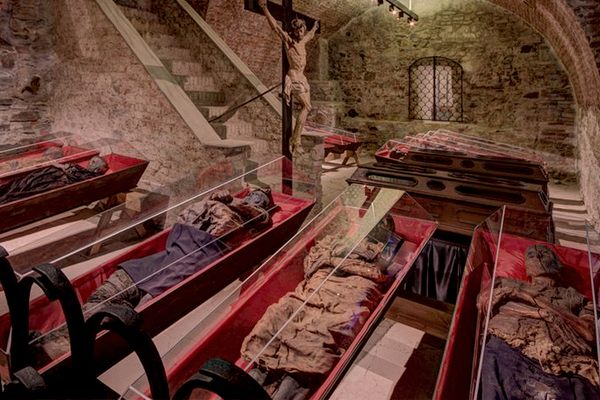
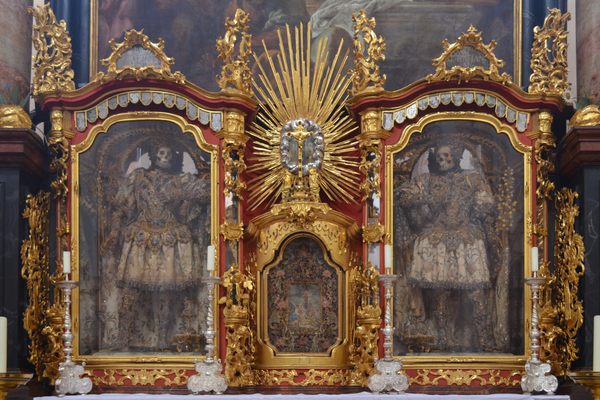
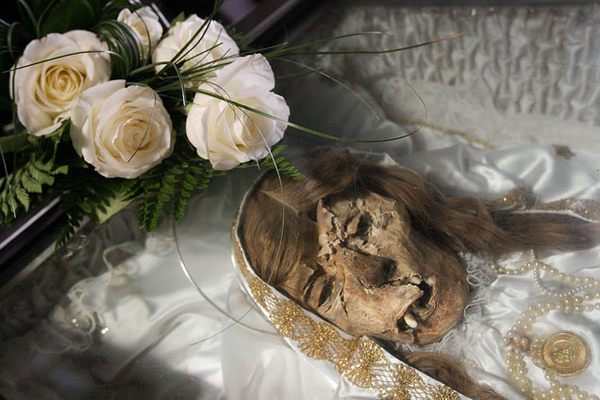
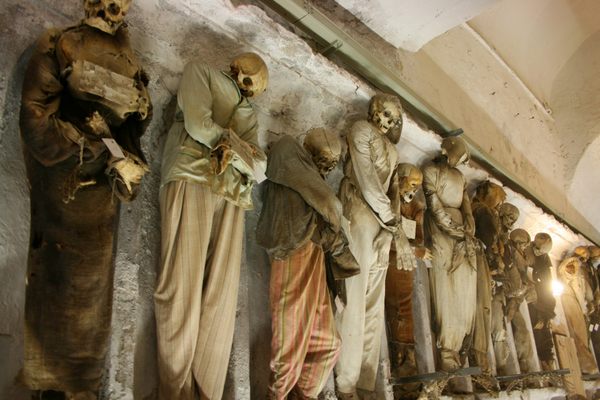
Mark Twain wrote about it in his 1869 book Innocents Abroad. When Twain asked one of the monks what would happen when he died, the monk responded, "We must all lie here at last." And lie there they do. Some 4,000 Capuchin friars who died between 1528 and 1870 are still lying, hanging, and generally adorning the Santa Maria della Concezione crypt in Rome.
In 1631, the Capuchin friars, so-called because of the "capuche" or hood attached to their religious habit, left the friary of St. Bonaventure near the Trevi Fountain and came to live at Santa Maria della Concezione, of which only the church and crypt remain. They were ordered by Cardinal Antonio Barberini (the Pope's brother and a member of the Capuchin order) to bring the remains of the deceased friars along with them to their new home so that all the Capuchin friars might be in one place.
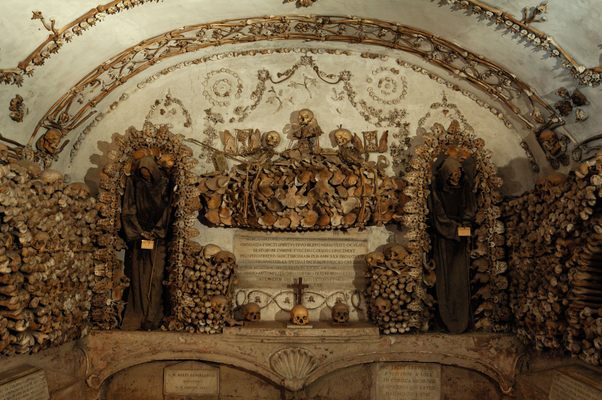
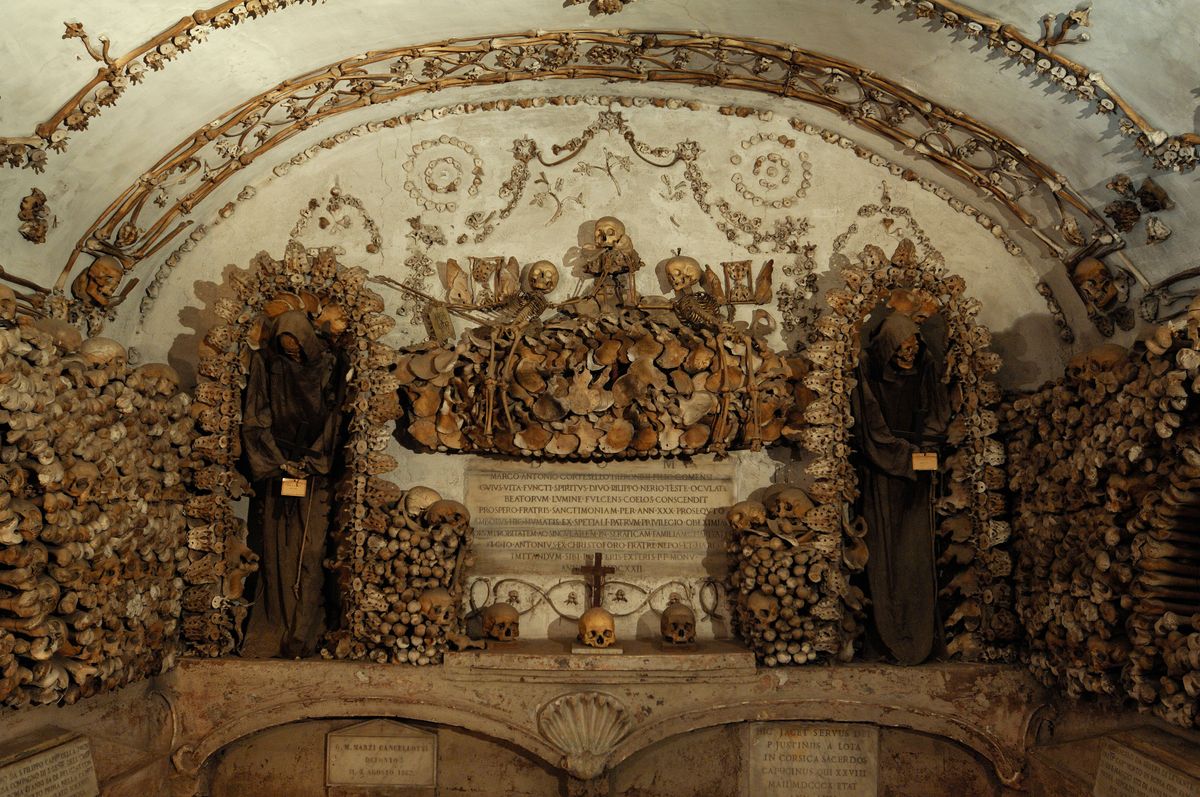
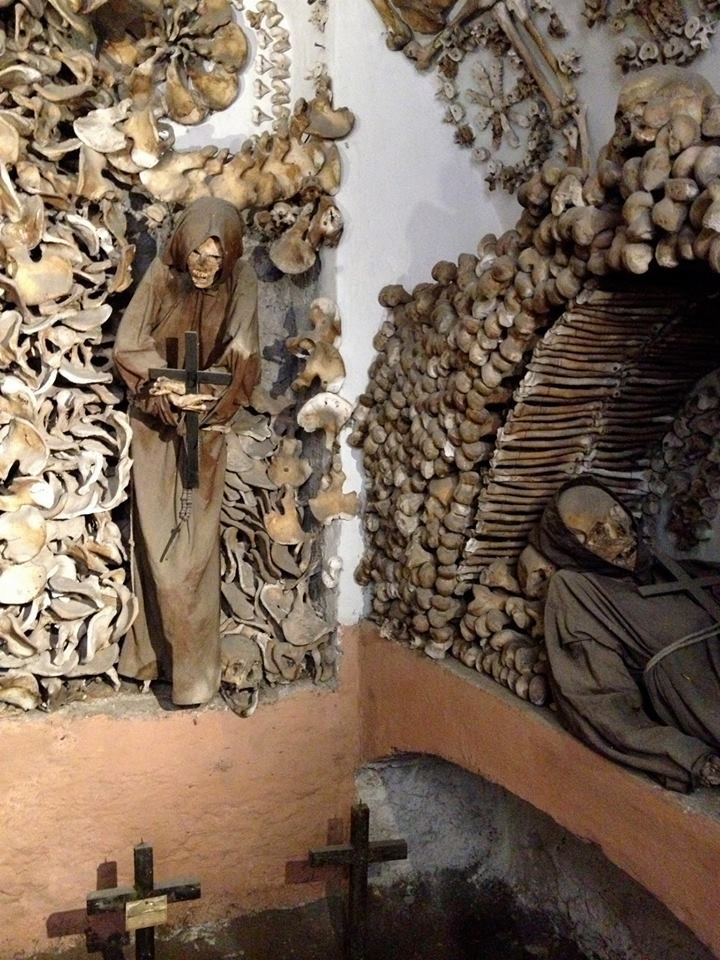
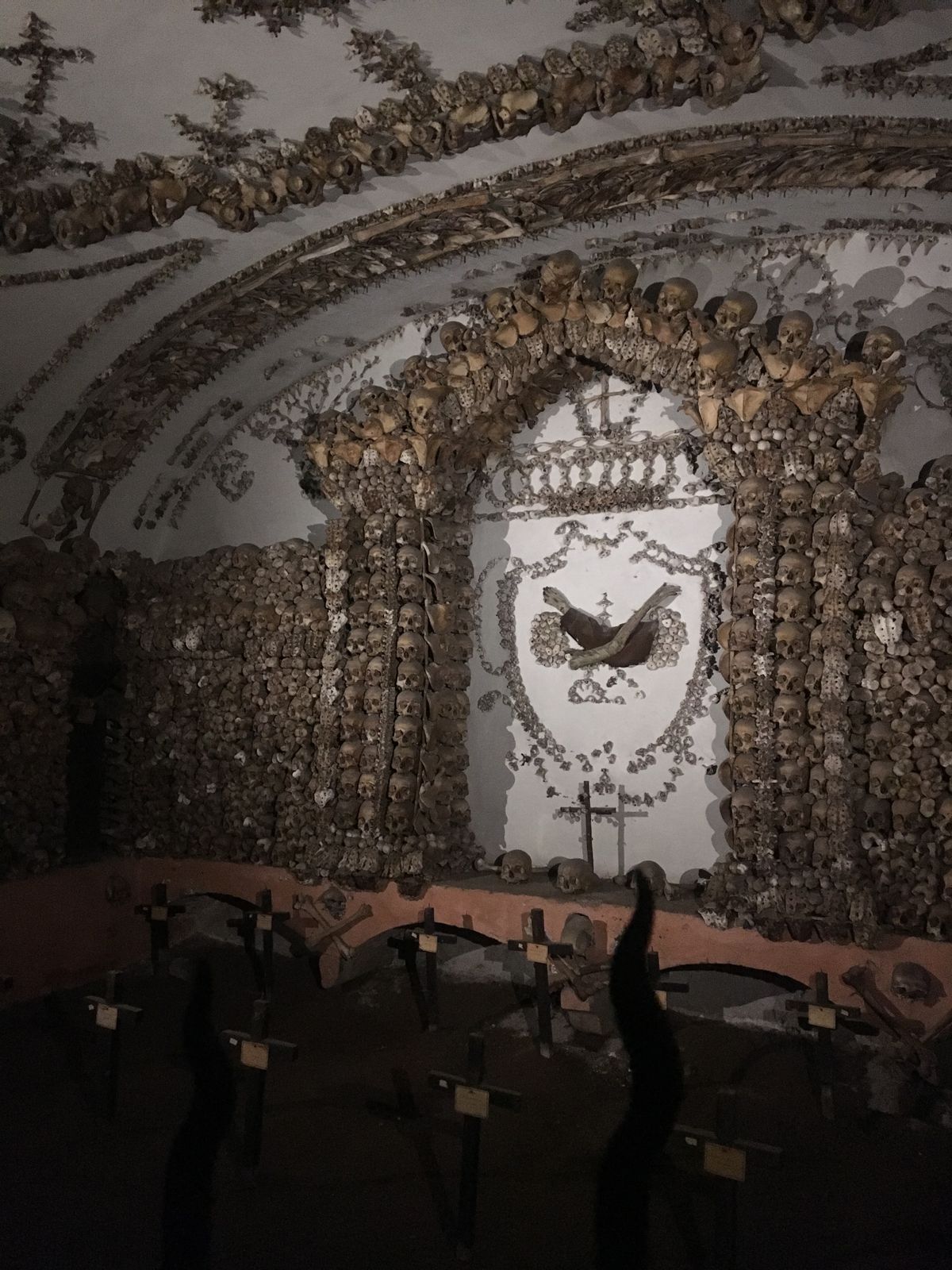
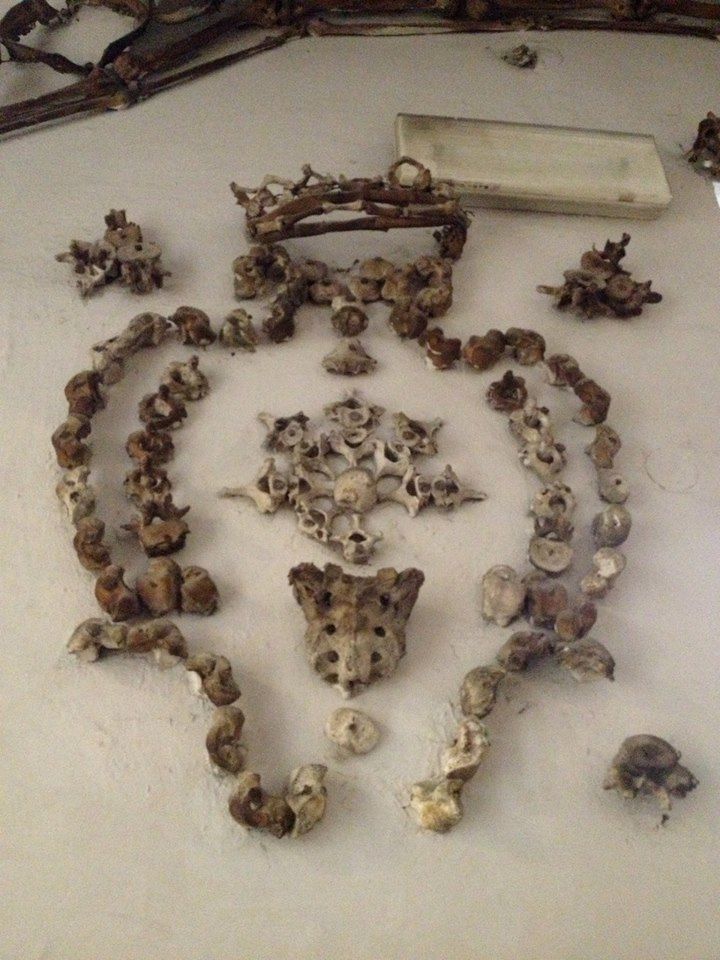
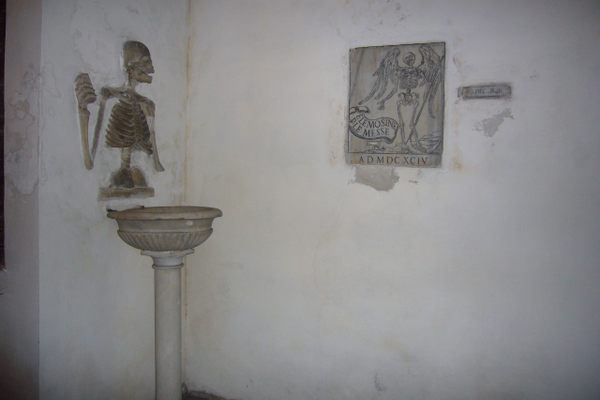
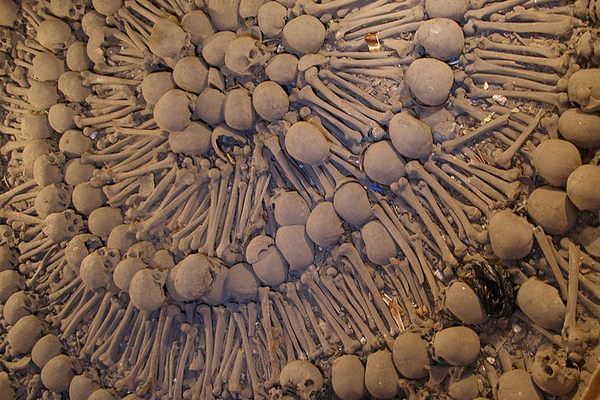
Rather than simply burying the remains of their dead brethren, the monks decorated the walls of the crypts with their bones as a way of reminding themselves that death could come at any time. A plaque in the crypt reads, "What you are now, we once were; what we are now, you shall be."
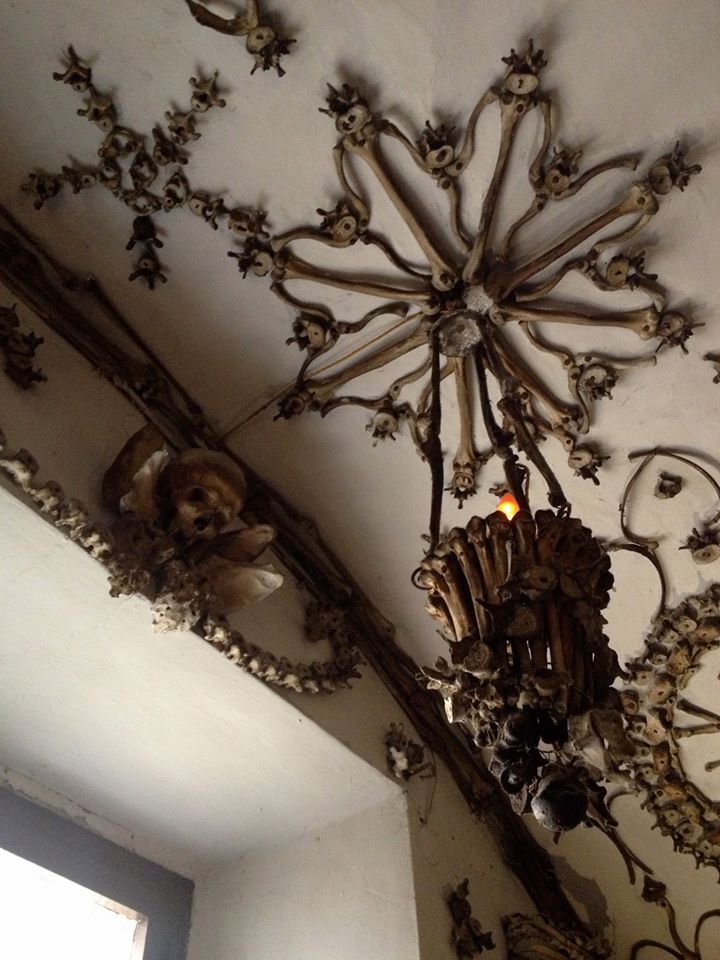
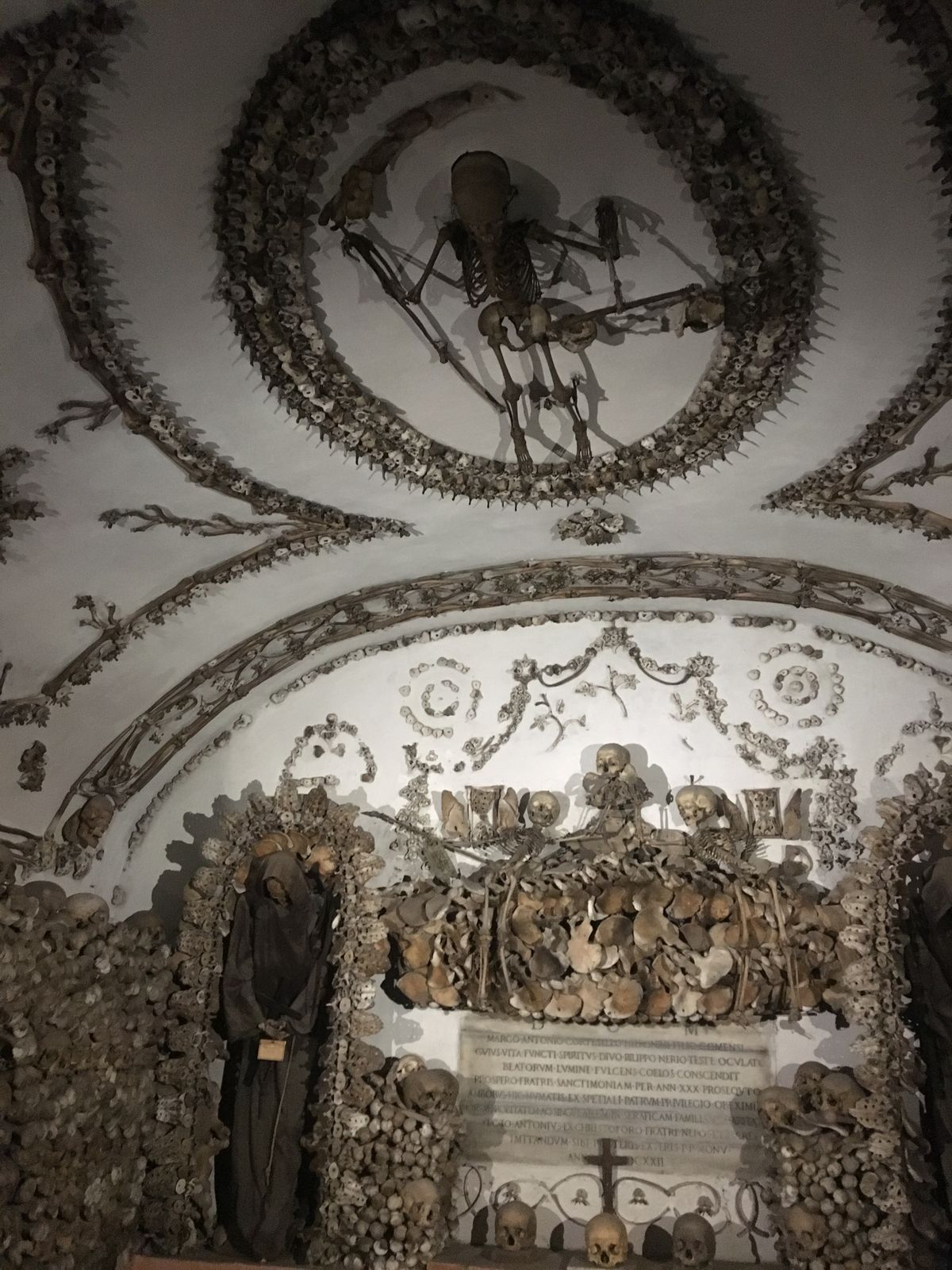
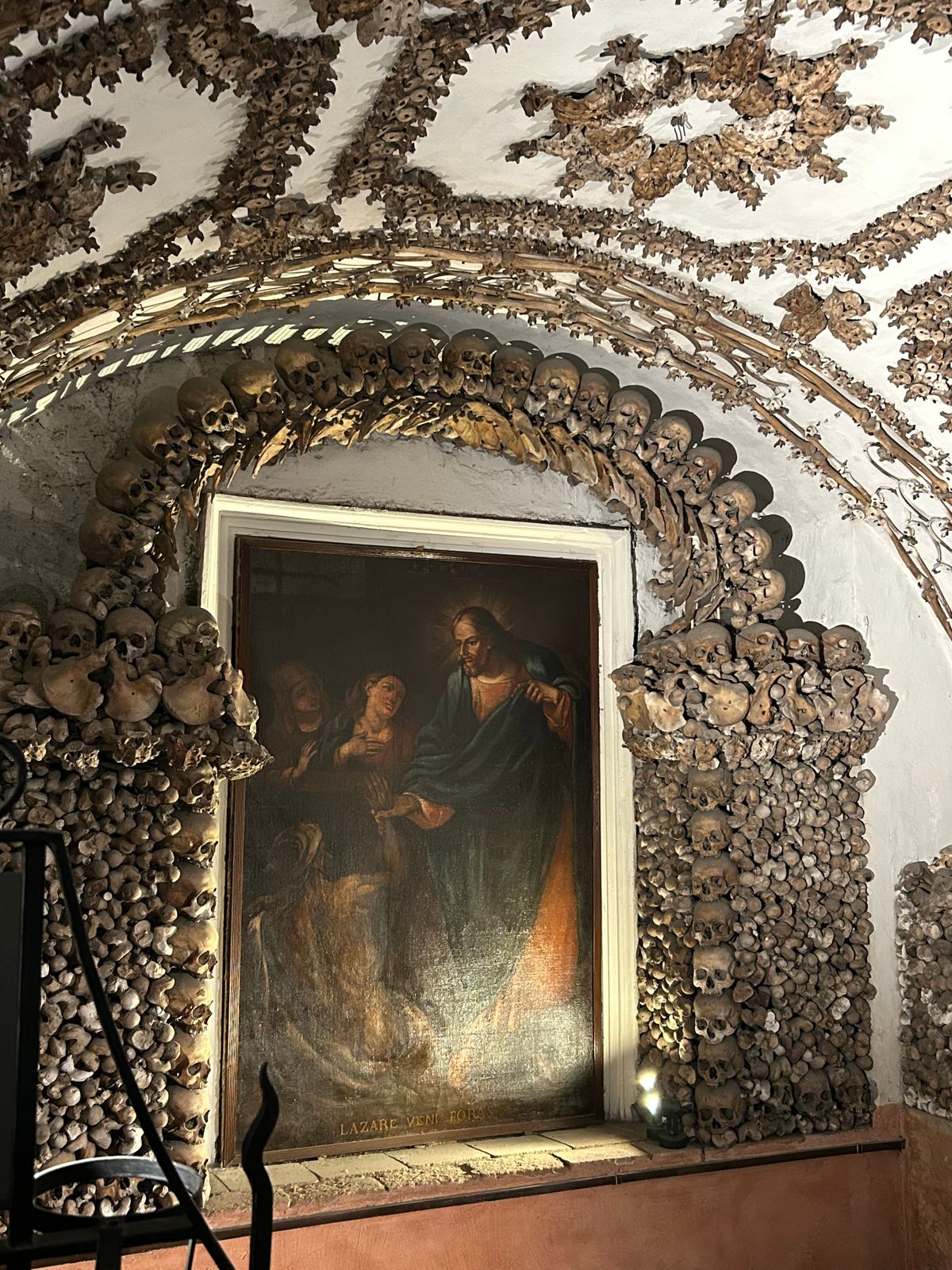
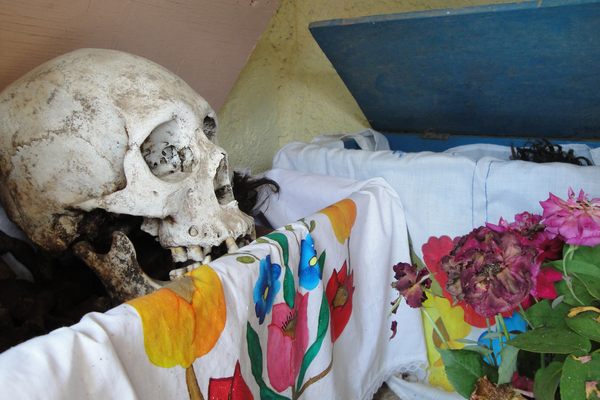
The ossuary contains a crypt of skulls, a crypt of leg bones, and perhaps the oddest—a "crypt of pelvises." Mummified monks were dressed in friar's clothes and hung from the walls and ceiling. With the addition of electricity, light fixtures were incorporated into some of the hanging monks, bringing a new meaning to the phrase "the eternal light."
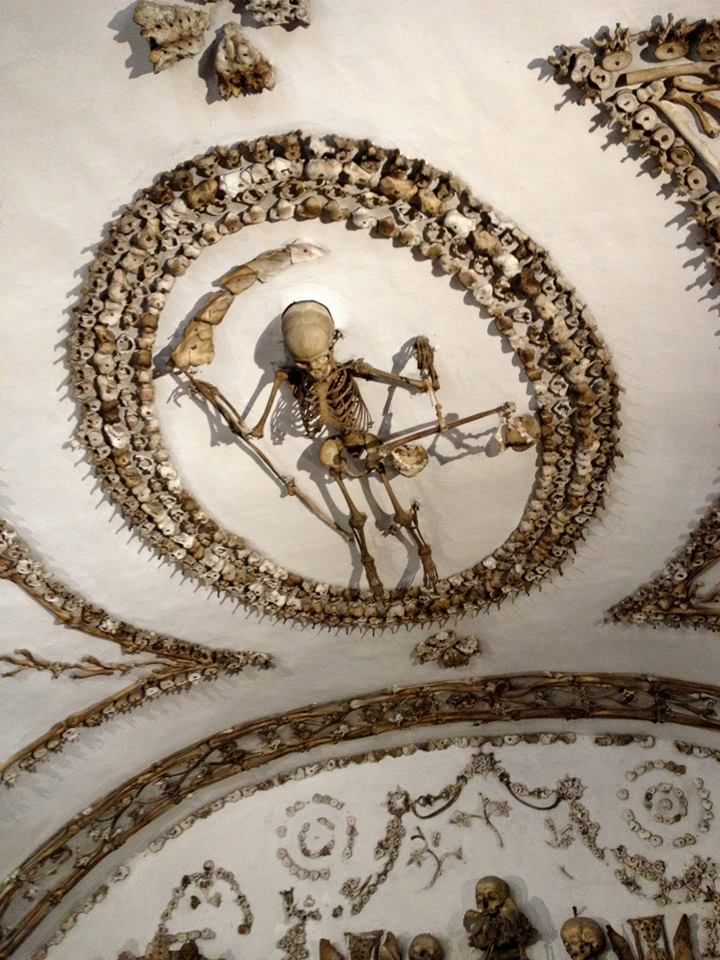
A particular highlight of the crypt is the skeleton enclosed in an oval of bones holding a scythe and scales—tools made entirely out of, yes, bones. The crypt is said to have been the inspiration for Sedlec Ossuary in the Czech Republic.
Related Tags
Know Before You Go
All photography is prohibited.
Flavors of Italy: Roman Carbonara, Florentine Steak & Venetian Cocktails
Savor local cuisine across Rome, Florence & Venice.
Book NowCommunity Contributors
Added By
Published
August 9, 2009